how many electrons in f orbital|Shells, subshells, and orbitals (video) : Bacolod Learn how multi-electron atoms behave and affect the atomic structure and . 6 pm PST ; 7 pm PST ; 8 pm PST ; 9 pm PST ; 10 pm PST ; 11 pm PST ; Thu. Sep5 +9. CEST / CET. Central European Summer .
how many electrons in f orbital,This means that the s orbital can contain up to two electrons, the p orbital can contain up to six electrons, the d orbital can contain up to 10 electrons, and the f orbital can contain up to 14 electrons.how many electrons in f orbitalLearn about the electron spin quantum number, the fourth quantum number for .Learn how multi-electron atoms behave and affect the atomic structure and .
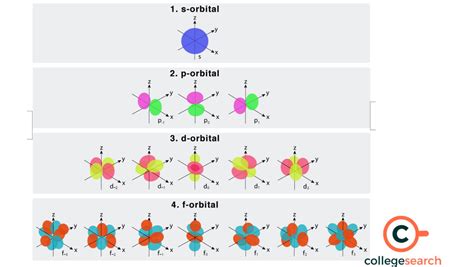
Learn about the shapes, sizes and capacities of s,p,d,f orbitals, the regions of space where electrons are most likely to be found. Find out how many electrons can s,p,d,f orbitals hold and see examples of .However, the question specifically asks for the maximum number of electrons in one such orbital, and any single atomic orbital, regardless of the sub-shell type specified by $l$, .The electrons in an atom are arranged in shells that surround the nucleus, with each successive shell being farther from the nucleus. Electron shells consist of one or more . Electron configurations and orbital diagrams can be determined by applying the Pauli exclusion principle (no two electrons can have the same set of four quantum numbers) and Hund’s rule . f orbital multilobed region of space with high electron density, describes orbitals with l = 3. An electron in this orbital is called an f electron magnetic quantum .
An orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own projection of spin . The simple names s orbital, p orbital, d orbital, and f orbital refer to orbitals with angular momentum quantum number .First, remember that each orbital, whether it is s, p, d, or f can accommodate two electrons at most. We can see this in orbital diagrams where the orbitals are shown as boxes and electrons as arrows, we .Every subshell has a # of orbits s/p/d/f that can each hold 2 electrons each (one has the opposite spin of the other). The first shell (of all atoms) has 1 subshell of s-orbitals containing 1 s orbital. This means that the first shell can hold 2 electrons. The second shell has 2 subshells: 1 s-orbital and 3 p-orbitals.
s-orbitals can hold 2 electrons, the p-orbitals can hold 6 electrons. Thus, the second shell can have 8 electrons. The n=3 (third) shell has: The 3s orbital; The 3p orbitals; The 3d orbitals; s-orbitals .Shells, subshells, and orbitals (video) 1 Answer. BRIAN M. May 26, 2014. The f orbital has 7 sub levels with the possibility of two electrons in each suborbital. Therefore, the f orbital can hold 14 electrons.How many electrons can an orbital of type f hold? A. 6 B. 10 C. 2 D. 14 E. 1. Since there can be [-ℓ, ℓ] orientations and since the orbital type f has ℓ = 3, we should have 7 possible orientations with 2 spins, so ${7 \times 2 = 14}$, so I thought the correct answer was D (14). However, I got it wrong and the correct answer is marked as C .
Figure 9.6.9 9.6. 9: Orbital filling diagrams for hydrogen, helium, and lithium. According to the Aufbau process, sublevels and orbitals are filled with electrons in order of increasing energy. Since the s s sublevel consists of just one orbital, the second electron simply pairs up with the first electron as in helium.The four chemically important types of atomic orbital correspond to values of l = 0, 1, 2, and 3. Orbitals with l = 0 are s orbitals and are spherically symmetrical, with the greatest probability of finding the electron occurring at the nucleus. All orbitals with values of n > 1 and l = 0 contain one or more nodes.how many electrons in f orbital Shells, subshells, and orbitals (video) 1 Answer. The f sublevel as a whole can hold up to 14 electrons due to the fact that it consists of 7 orbitals, but each one can only hold up to 2 electrons. 2 electrons ---> see below: The f sublevel as a whole can hold up to 14 electrons due to the fact that it consists of 7 orbitals, but each one can only hold up to 2 electrons. The Azimuthal Quantum Number. The second quantum number is often called the azimuthal quantum number (l).The value of l describes the shape of the region of space occupied by the electron. The allowed values of l depend on the value of n and can range from 0 to n − 1: \[l = 0, 1, 2,., n − 1 \label{6.5.2}\]
These are arbitrarily given the symbols px, py and pz. This is simply for convenience; the x, y, and z directions change constantly as the atom tumbles in space. Figure 3: Hydrogen's electron - the 2p orbitals. The p orbitals at the second energy level are called 2p x, 2p y and 2p z. There are similar orbitals at subsequent levels: 3p x, 3p y .The subshells s, p, d, and f contain the following number of orbitals respectively, where every orbital can hold up to two electrons maximum: s: 1 orbital, 2 electrons. p: 3 orbitals, 6 electrons.If an electron has an orbital angular momentum of 7.892 x 10-34 Js, what is the orbital quantum number for the state of the electron? How many valence electrons does promethium have? How many orbitals are contained in the third principal level (n=3) of .
If there are more electrons after the 1s, and 2s orbitals have been filled, each p orbital will be filled with one electron first before two electrons try to reside in the same p orbital. This is known as Hund's rule. .

It should be 14 electrons. The f subshell has a total of seven orbitals, and each orbital can hold two electrons, and so the f subshell can hold a total of 7*2=14 electrons. . How many electrons can occupy the f orbitals at each energy level? Chemistry Electron Configuration s,p,d,f Orbitals. 1 Answer Nam D. Mar 20, 2018

F orbitals are the orbitals that, in total, have the affinity to accommodate 14 electrons in them. The shape of the f orbital is tetrahedral. Though the shape of the f orbital is more complex than the other orbitals, the rule of filling the orbital remains the same as that of p and the d orbitals. The alignment of the electrons is also found to .F orbitals are the orbitals that, in total, have the affinity to accommodate 14 electrons in them. The shape of the f orbital is tetrahedral. Though the shape of the f orbital is more complex than the other orbitals, the rule of filling the orbital remains the same as that of p and the d orbitals. The alignment of the electrons is also found to .
When fluorine atoms are excited, then fluorine atoms absorb energy. As a result, an electron in the 2p y orbital jumps to the 3s orbital. Therefore, the electron configuration of fluorine(F*) in an excited state will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p x 2 2p y 1 2p z 1 3s 1. Fluoride ion(F –) electron configurationEach orbital can hold two electrons. They are also known as atomic orbitals. Atomic orbitals come in different shapes, depending on how much energy and angular momentum is associated with that orbital. We will learn about the shapes of s, p, d, and f orbitals. The precise definition of an orbital, is a complex valued mathematical function that .The tiny superscripts say how many electrons live in each orbital, the letters represent the orbitals that are available, and the big numbers say which energy level the orbitals are found in. Remember that the total number of electrons just equals the total number of protons, and so the superscripts add up to 8, the atomic number of oxygen .
On the far left of Figure 3.6.1 3.6. 1 are the highest energy electromagnetic waves. These are called gamma rays and can be quite dangerous, in large numbers, to living systems. The next lower energy form of electromagnetic waves are called x-rays. Most of you are familiar with the penetration abilities of these waves.
how many electrons in f orbital|Shells, subshells, and orbitals (video)
PH0 · s,p,d,f Orbitals
PH1 · s, p, d, f Atomic Orbitals
PH2 · The periodic table, electron shells, and orbitals
PH3 · Shells, subshells, and orbitals (video)
PH4 · How many electrons can an orbital of type f hold?
PH5 · For s, p, d, and f orbitals, how many electrons can each hold?
PH6 · Electronic Orbitals
PH7 · Atomic orbital
PH8 · 8.3: Electron Configurations
PH9 · 5.7: Atomic Orbitals and Quantum Numbers